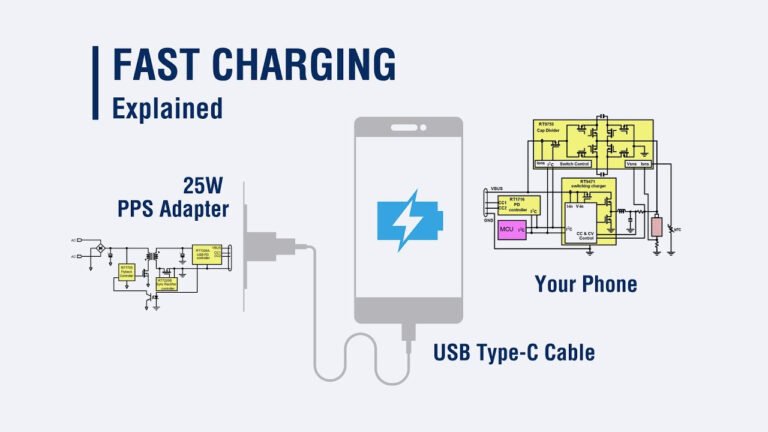
The reason why mobile phones charge so quickly is because of fast charging. We all know about fast charging, but do you how it works?
The charger circuit based on the PD protocol can keep the AC/DC part unchanged, but replace the QC protocol controller with a PD controller.
What is the PD fast charging protocol?
The PD charging protocol is a power transmission protocol announced by the USB-IF organization. It can increase the current default maximum power of the type-c interface from 5V/2A to 100W. At the same time, Google announced that the fast charging protocol carried by mobile phones above Android 7.0 must support the PD protocol, aiming to unify the fast charging market.

What does PD charging protocol mean?
What does PD charging protocol mean?
USB-Power Delivery (USBPD) is one of the current mainstream fast charging protocols and is a fast charging specification developed by the USB-IF organization. USB PD increases power delivery through USB cables and connectors, expanding the cable bus power supply capabilities in USB applications. This specification can achieve higher voltages and currents, with a maximum power delivery of 100 watts, and can freely change the direction of power delivery.
| Technology | Voltage | Current | Maximum Power | Release Date | SoC Models |
| QC 1.0 | 5V | 2A | 10W | 2013 | Snapdragon 600 |
| QC 2.0 | 5V, 9V, 12V | 2A, 2A, 1.67A | 18W | 2015 | Snapdragon 200, 208, 210, 212, 400, 410, 412, 415, 425, 610, 615, 616, 800, 801, 805, 808, 810 |
| QC 3.0 | 3.6V to 20V, 200mV dynamic adjustment | 2.5A or 4.6A | 22W | 2016 | Snapdragon 427, 430, 435, 617, 620, 625, 626, 650, 652, 653, 820, 821 |
| QC 4.0 | ? | ? | 28W | 2017 | Snapdragon 835, 660, 636 |
| QC 4.0+ | 5V, 9V (USB-PD), 3V to 5.9V or 3V to 11V, 20mV increments (USB-PD 3.0 optional power supply), 3.6V to 20V, 200mV increments (QC charger) | 3A (USB-PD), 2.5A or 4.6A (QC) | 27W (USB-PD) | 2017 | Snapdragon 845 |
The relationship between USB PD and Type-C
People often talk about USB PD and Type-C together, and even call Type-C chargers PD chargers. USB PD and Type-C are actually two different things. USB PD is a fast charging protocol, while Type-C is a new interface specification.
The Type-C interface supports a maximum of 5V/3A by default, but after implementing the USB PD protocol, the output power can be supported up to 100W. Therefore, many devices with Type-C interfaces now support the USB PD protocol.
Advantages of PD fast charging protocol
PD stands for Power Delivery, which focuses on the power transmission process between two or more devices, or even a smart grid based on the USB interface. The power transmission can be bidirectional, even networked, and can have a system-level power supply strategy. QC stands for Quick Charge, which only focuses on fast charging. The power transmission is unidirectional , does not have the power networking capability, and does not support other functions except power supply.
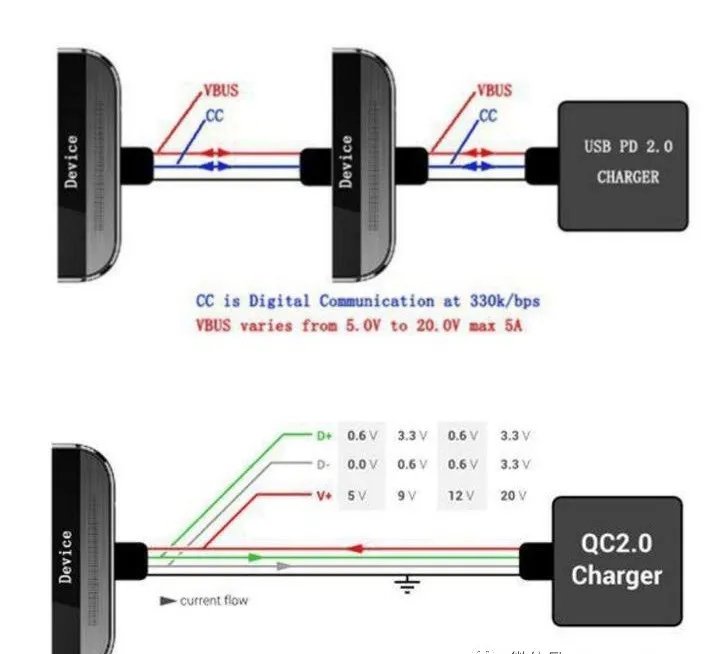
Of course, many people still don’t understand the significance of it after reading it. Simply put it, if the PD protocol becomes popular, you can go back to the good old days when you only needed one charger to charge all your mobile phones at home. Even better is that this charger can also charge your computer and tablet, and the mobile phone can also be transformed into a mobile power source.
USB PD fast charging communication principle
USB PD communication is the process of modulating the message of the protocol layer into a 24MHZ FSK signal and coupling it to VBUS, or obtaining the FSK signal from VBUS to realize the communication between the mobile phone and the charger.
As shown in the figure below, in USB PD communication, the 24MHz FSK is coupled to the DC level on VBUS through the cAC-Coupling coupling capacitor. In order to prevent the 24MHz FSK from affecting the VBUS DC voltage of PowerSupply or USBHost , a low-pass filter composed of zIsolation inductors is added to the loop to filter out the FSK signal.
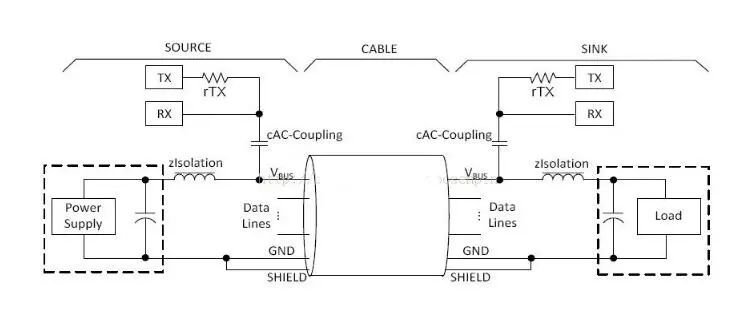
The principle of USB PD is explained as follows, taking the example that both the mobile phone and the charger support USB PD:
1) The PHY of USBOTG monitors the VBUS voltage. If there is a 5V voltage of VBUS and it is detected that the OTGID pin is a 1K pull-down resistor (not in OTG Home mode, the ID resistance of OTG Home mode is less than 1K), it means that the cable supports USBPD;
2) USBOTG performs normal BCSV1.2 charger detection and starts the USBPD device policy manager. The policy manager monitors whether the FSK signal is coupled to the DC level of VBUS, and decodes the message to obtain the CapabilitiesSource message. It parses the message according to the USBPD specification to obtain a list of all voltage and current pairs supported by the USBPD charger.
3) The mobile phone selects a voltage and current pair from the CapabilitiesSource message according to the user’s configuration and adds the voltage and current pair to the payload of the Request message. The policy manager then couples the FSK signal to the VBUS DC level.
4) The charger decodes the FSK signal and sends an Accept message to the phone, while adjusting the DC voltage and current output of PowerSupply;
5) The mobile phone receives the Accept message and adjusts the charging voltage and current of the ChargerIC;
6) During the charging process, the mobile phone can dynamically send a Request message to request the charger to change the output voltage and current, thereby achieving a fast charging process.